One afternoon sitting in my study, I was watching a video of Swami Sarvapriyananda about Practical Methods of Meditation. He spoke eloquently about the 3 Vedantic pillars - श्र्वण, मनन, निधिध्यासन (Shravana, Manana, Nidhidhyasana), the learning framework in Advaita Vedanta – the framework for gaining knowledge, reflecting back on the same and putting it into practice. That is when it dawned on me the lucid relationship between the three Vedantic pillars and Design Thinking.
I sat down and spent the whole afternoon and a good part of the evening and took a deeper look at the parallels between the two. In this document, I am elaborating my analysis of the relationship between the two. There are several definitions of Design Thinking and the following are a couple of them
Design thinking is a human-centered approach to innovation that integrates the needs of people, the possibilities of technology, and the requirements for business success - Tim Brown, CEO, IDEO
Design thinking is the mindset that aims to improve the situation of people through the experiences they have - Herbert Simon (Nobel Laurate in Economics
In this article, I am attempting to relate the 3 Iterative Vedantic Pillars of gaining knowledge - श्र्वण, मनन, निधिध्यासन and the 5 iterative stages and the 3 Core Criteriums of design thinking and the beautiful connection between the 1000s of years old Vedantic knowledge and a few decades old Design Thinking Approach
At its core, Design Thinking is an approach to learn and implement new ways of moving from current reality towards new goals by identifying options and taking action.
A few notes
All learnings are based on experience and reflecting back on experience.
Learning is an iterative process. In the sense, we experience something, and learn from that experience. Based on whether our experience meets our expectations or not, we design some changes to our behaviours which in turn will change our experience. We continue this cycle until we are happy with what we are experiencing
The test bed for our design and our learning is how and what we experience
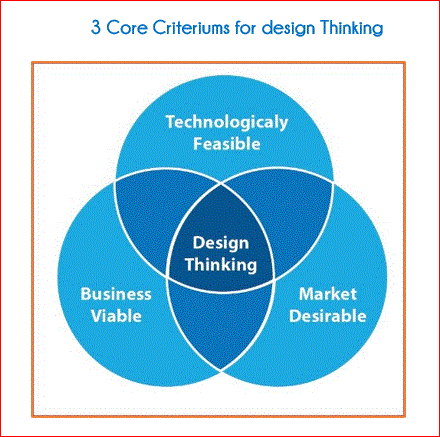
The experiences can be in the form of ‘What we desire psychologically”, What we expect in terms of monetary or business / market” and “How easy is this to implement and use” – These in other words are what in my view is defined as 3 Core Criteriums – Human Desirability, Business Viability and Technological Feasibility.
The ‘we’ in this is human.
In every aspect, it is the human experience that provides a sounding board.
At the core of all these experiences is the human desire to experience peace or Shanti as it is called in Sanskrit
3 Pillars of Vedantic Practice for Knowledge
श्र्वण, मनन, निधिध्यासन
श्र्वण
Observing
Authentic listening to understand, collect facts and figures, opinions, perceptions, observations
मनन
Absorbing
Understanding concepts, asking insightful and empowering questions, seeking clarifications, resolving conflicts, observing patterns / adverse patterns, identifying blockers, inherited and cognitive biases, intellectual dishonesty
निधिध्यासन
Internalising
Contemplating, connecting the dots, removing belief blockers, experiencing peace
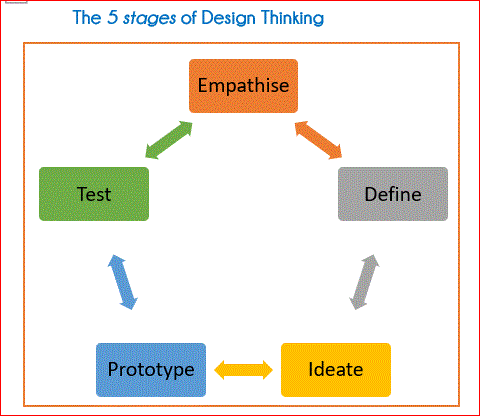
Connecting the Dots between the three Vedantic Pillars and the 5 Stages of Design Thinking
Moving between the 3 Pillars and the 5 Stages is not linear. During the Design Thinking Process, the participants move forward and back between these pillars / stages multiple times.
The practice of Design Thinking requires
Atmavichara – Self Reflection and
साधना = साध्यम् + साधनम् Which when translated in English is
Methodical discipline to attain & practice desired knowledge = Goal + Instrument / Tool
To name a few tools that can be used during the various stages of Design thinking:
Brainstorming – There are multiple types of brainstorming and can be used based on need. Some of the popular ones are listed below along with a link to a couple of less common ones
Round Robin Approach – Using Flip Chart or a Paper on which ideas are listed down - https://www.mindtools.com/brainstm.html
Brainwriting - https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newCT_86.htm
Alphabet Brainstorming - http://www.edusolutions21.com/files/106591268.pdf
Six Thinking Hats is great tool to ideate and test options
SCAMPER can be used with great effect to explore possibilities -https://www.mindtools.com/pages/article/newCT_02.htm
The above is not a comprehensive list of such tools and there are many more such tools that can used effectively.
The key to successfully innovate from ideas to action is to adhere to the iterative process and structure of Shravana, Manana, Nidhidhyasana / Design Thinking.
Finally, a quick look at the overlaps between the key Features of the two practices – The 3 Vedantic Pillars and Design Thinking.
Thanks for reading this article. Please do share your thoughts and feedback

Comentários